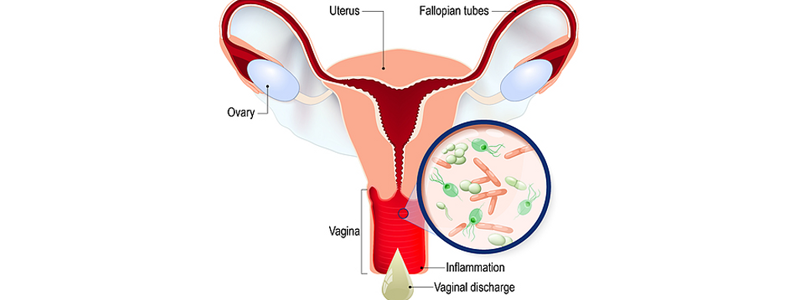
Vaginal infections are common health issues that affect many women at some point in their lives. These infections can be caused by various factors, including bacteria, yeast, and viruses. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for vaginal infections is crucial for maintaining women's reproductive health and overall well-being.
BV is a common bacterial infection that occurs when there is an imbalance in the natural bacteria present in the vagina. The overgrowth of harmful bacteria can lead to symptoms such as unusual discharge, itching, and a characteristic fishy odor.
Candida, a type of yeast, is normally present in the vagina. However, an overgrowth of yeast can lead to a yeast infection. Factors such as antibiotics, hormonal changes, and a weakened immune system can contribute to the development of yeast infections, characterized by itching, redness, and a thick, white discharge.
This sexually transmitted infection (STI) is caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Symptoms include itching, burning, and a frothy, greenish-yellow discharge. Both sexual and non-sexual transmission can occur.
Certain viruses, such as the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and human papillomavirus (HPV), can cause vaginal infections. These infections may present with lesions, ulcers, or warts in the genital area.
The symptoms of vaginal infections can vary depending on the type of infection, but common signs include:
Changes in the color, consistency, or odor of vaginal discharge can indicate an infection.
Persistent itching or irritation in the vaginal area may be a symptom of infection.
Pain during urination or sexual intercourse can be indicative of a vaginal infection.
Inflammation of the vaginal tissues may lead to redness and swelling.
Bacterial infections like BV and certain STIs can be treated with antibiotics. It's crucial to complete the full course of medication, even if symptoms improve before completion.
Yeast infections are commonly treated with antifungal medications, available in various forms such as creams, suppositories, or oral tablets.
Trichomoniasis is typically treated with antiparasitic medications prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Viral infections, such as herpes or HPV, may require antiviral medications to manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Using condoms can help prevent the transmission of STIs, reducing the risk of vaginal infections.
Gentle washing with mild, fragrance-free soap and avoiding douching can help maintain a healthy vaginal environment.
Cotton underwear allows for better air circulation, reducing the risk of moisture buildup that can contribute to infections.
Routine gynecological check-ups can help detect and address potential infections early on.
Vaginal infections are common but treatable conditions that can significantly impact women's health and quality of life. Seeking prompt medical attention, practicing preventive measures, and maintaining good vaginal hygiene are essential for the prevention and effective management of these infections. Women should be encouraged to communicate openly with healthcare providers to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment, promoting overall reproductive health and well-being.