Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals with ovaries, particularly during their reproductive years. It is characterized by a range of symptoms and hormonal imbalances that can impact various aspects of health, including menstrual cycles, fertility, and metabolic function. In this comprehensive overview, we delve into the complexities of PCOS, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and potential treatment options.
PCOS is a multifaceted condition that involves the disruption of normal ovarian function, leading to hormonal imbalances and a variety of associated symptoms. It is one of the most common endocrine disorders affecting people assigned female at birth and can manifest differently in each individual.
One of the hallmark features of PCOS is irregular or absent menstrual cycles. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt the normal ovulatory process, leading to irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) are commonly observed in individuals with PCOS. This hormonal imbalance can contribute to symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (excess hair growth), and male-pattern baldness.
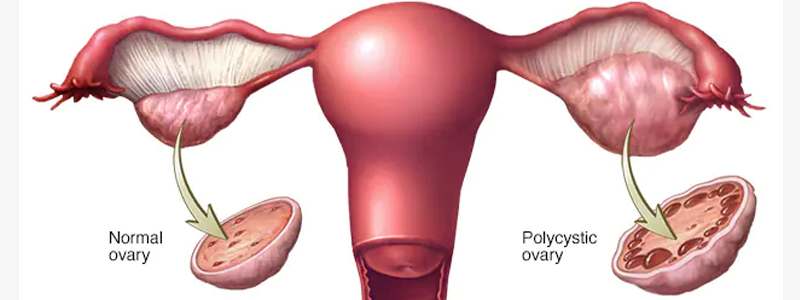
On ultrasound imaging, polycystic ovaries may appear enlarged and contain multiple small follicles. However, the presence of polycystic ovaries alone does not necessarily indicate PCOS, as other criteria must also be met for a diagnosis.
While the exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to contribute to its development. The following factors may increase the risk of PCOS:
A family history of PCOS may increase the likelihood of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic component.
Insulin resistance, a condition in which cells do not respond effectively to insulin, is commonly associated with PCOS. This can lead to elevated insulin levels, contributing to hormonal imbalances.
Obesity and sedentary lifestyle may exacerbate insulin resistance and contribute to the development or worsening of PCOS symptoms.
Diagnosing PCOS involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, symptoms, and laboratory tests. The following criteria are commonly used for diagnosis:
Irregular menstrual cycles or anovulation (lack of ovulation) is a key criterion for diagnosing PCOS.
Clinical signs of elevated androgen levels, such as acne, hirsutism, or male-pattern baldness, contribute to the diagnosis.
Transvaginal ultrasound may reveal polycystic ovaries, but this is not the sole criterion for diagnosis.
The management of PCOS is tailored to address individual symptoms and concerns. Treatment options include:
Implementing healthy lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management, can help improve insulin sensitivity and alleviate symptoms.
Hormonal contraceptives, anti-androgen medications, and insulin-sensitizing agents may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and address insulin resistance.
For individuals trying to conceive, fertility treatments such as ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
Symptomatic management may involve treatments for acne, hirsutism, and hair loss.
PCOS is associated with long-term health implications that extend beyond reproductive health. Individuals with PCOS have a higher risk of developing conditions such as:
Insulin resistance in PCOS increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
PCOS is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly in individuals with obesity.
Prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen due to irregular menstrual cycles may increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
PCOS is a complex and heterogeneous condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and management. By addressing symptoms, supporting lifestyle modifications, and managing long-term health risks, healthcare providers can work collaboratively with individuals with PCOS to enhance overall well-being and empower them to navigate the challenges associated with this common hormonal disorder.
To Know more about Women Healthcare & Treatment, Contact Dr Archana Rajendran, the leading & finest Gynaecologist & Obstetrician in Thane West for PCOD / PCOS Treatment.